If you’re wondering why your listings on Used-Line.com generate many VIEWS, but a very low CTR (Clickthrough Rate) with a decided lack in RFQs, then you are asking the right questions.
How do you check if your ad (listing) is getting the views but not the clickthroughs?
Used-Line now offers a Statistics service that can show you all the activity taking place on your listings – both individual and overall listings. We previously discussed how to write a good sell ad for Used-Line. Now let’s find out if you really do need to work on your ads – or if, in fact, you are doing OK.
The new Used-Line Statistics service can tell you how your listings are doing by providing you with:
- Instant views of the effectiveness of your listings overall
- The ability to drill down into the specific statistics of individual ads
Okay. So how do we retrieve all this important information?
To view overall Statistics of all your Used-Line listings for each month
- Log in to your Used-Line account.
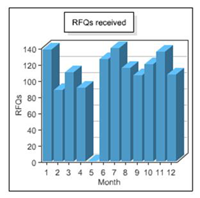
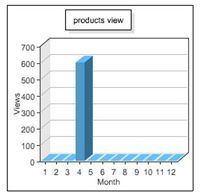
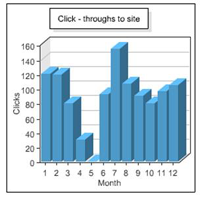
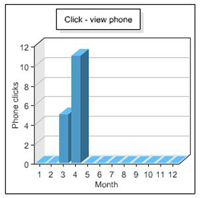
- To view overall statistics of all your listings, click Statistics under My Used-Line on the left side of the page. View statistics for your total listings for each month in the following four graphs:
- RFQs received: Indicates how many Used-Line buyers sent you a Request for Quote (RFQ) for items you advertised.
- Views – product pages: Indicates how many potential buyers saw your postings.
- Click-throughs to site: Indicates how many Used-Line visitors visited your company website.
- Click – view phone: Indicates how many Used-Line visitors clicked the Seller phone number button in your ads.
- RFQs received: Indicates how many Used-Line buyers sent you a Request for Quote (RFQ) for items you advertised.
To view statistics for your individual listings
- If you have not already done so, log in to your Used-Line account.
- To view individual listing statistics, click My Ads under My Used-Line on the left side of the page. Each ad is in the ItemID column in the My Ads tab. You can view the specific statistics for each of your ads in the four columns to the right of the ItemId column:
- Views: The number of potential buyers that viewed the ad since it was first posted
- Site: The number of Used-Line visitors that visited your company website by clicking the Visit Website button in the ad
- RFQ: The number of RFQs that have been sent for the item you described in the ad
- Phone: The number of Used-Line visitors that have clicked the Seller phone number button in the ad
Note: At times, you may want to update a listing because of new or changed information. This is fine, as long as you realize that your listing will be reset. When a listing is reset, the statistics for that listing are reset. As a result, only the statistics for the most recent version of your ad will be shown.
So, let’s get tracking!